Description
Determining a fire danger is the basis for all most advanced wildfire prevention services. Risk forecast indexes are estimated once the morphology of the ground, the relevant weather measurements detected by the remote measurement network stations and the characteristics of the vegetation are known. They always comprise a FC (Fuel Code) component associated with the structure of the vegetation and biomass, a MC (Meteo Code) component which takes into account the weather parameters and a TC (Topological Code) component that describes the topography of the relevant area. Forecast indicators are all based on the assumption that the probability of ignition strictly depends on the hydration level of dead vegetable combustible matter, which in turn depends on the weather. In addition to the weather component, fires also strongly depend on the type and distribution of vegetation and the characteristics of the landscape; the distribution of human activities also cannot be neglected, varying from area to area, and giving each monitored territory its peculiarities. The CAE system provides risk indexes to the users, highlighting the probability of fire ignition on the monitored landscape and determining the difficulty in fighting the fire when it occurs, therefore providing extremely effective tools from the operating point of view in practical applications for fire management.
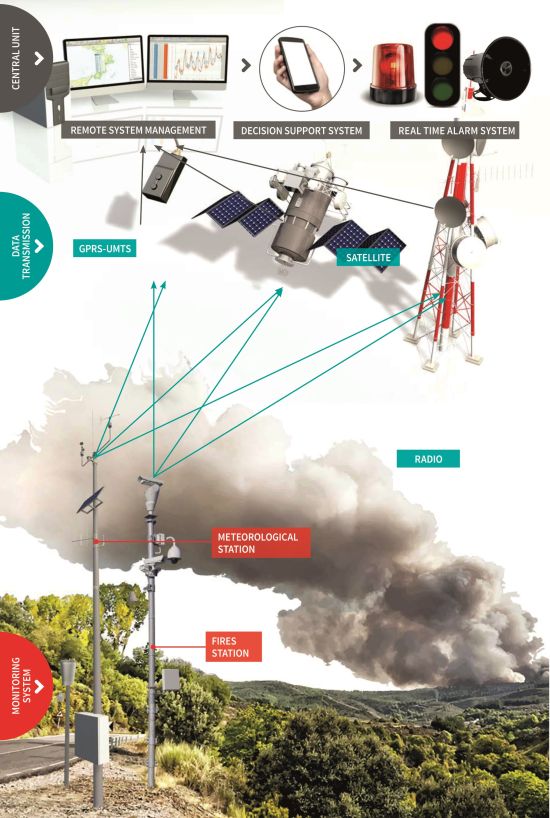
main measurements
- Wind speed and direction
- Brightness and irradiation
- Measured precipitations
- Air temperature and humidity
Case history

PUGLIA REGION - ARIF
Puglia's regional wooded area presents a high fire risk whilst fire-fighting operations are very complex continueTransmission System
- GSM/GPRS
- Radio Transmission
- Satellite Transmission
- WSN - W-Master & W-Point
- ACTI-Link
Other Sensors
- Albedometer AB20/K
- Anemometer AS202D
- Anemometer VV20 and DV20
- Evaporimeter E200
- Radiometer
- Pyranometer HE20K
- Thermo-Hygrometer TU20
- THS Thermo-Hygrometer
Customers